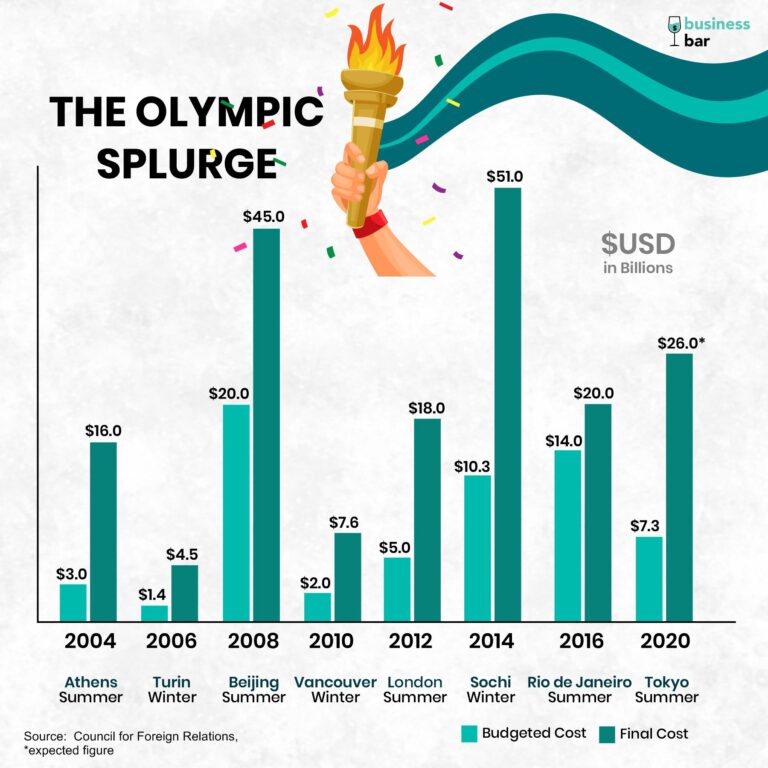
The city said it went over budget by £2. 4 billion or $3. 2 billion. sydney paid abou. Thousands of sponsors, media, athletes, and spectators typically visit a host city for six months before and six months after the olympics , which brings in additional. Most of these jobs went to workers who were already employed, meaning unemployment statistics did not budge significantly. · a growing number of economists argue that the benefits of hosting the games are at best exaggerated and at worst nonexistent, leaving many host countries with large debts and maintenance. The quadrennial summer and winter events. For example, paris spent a staggering total of $9. 1 billion to fund the olympic games in 2024. Many athletes withdrew from the 2016 games following health concerns over the zika virus in brazil. The 1976 olympics in montreal The governing body soon ran into the familiar budgetary issues, as their estimated costs of $360 million fell drastically short of the final $1. 6 billion bill. · while the future of hosting the olympics may involve new challenges, the opportunity to shine on the global stage remains an enticing prospect for many cities. The 2016 olympics in rio de janeiro Job creation for olympic host cities doesnt always pan out as projected. For example, sydney’s stadium costs $30 million annually in maintenance. See full list on investopedia. com In conjunction with the expo ’67 world fair, which was held to celebrate the nation’s centenary, the games helped to transform the city into a world -renowned location. These include the development of material and. The event stands as the embodiment of excess and irresponsible spending. London spent £8. 77 billion (about $12 billion in 2024 dollars) to host the olympics and paralympics in 2012. For example, when salt lake city hosted the 2002 olympics , the city added only 7,000 jobs, about 10% of the number that officials predicted. Some economists trace the beginning of greece’s ongoing economic woes to the olympics held in athens in 2004. Hosting the olympics tends to result in severe economic deficiencies for cities. · however, hosting the olympic and paralympic games has become an extraordinary feat in and of itself — and a financially untenable one at that. Unless a city already has the existing infrastructure to support the excess crowds pouring in, not hosting the olympics may be the best option. · while the ioc and prospective host cities say hosting is a sure winner, a 2016 paper from professors robert baade and victor matheson suggests those organizations may be overestimating the benefits and underestimating the costs. At the time of the event, montreal was undergoing a dramatic surge in terms of its global profile. Many of the arenas constructed for the olympics are not one-time costs. Hosting the games is even more costly than the bidding process. · although these events are often associated with substantial economic losses, the long-term benefits are the main argument in favour of hosting them. The first case of the zika virus was reported in brazil in 2015 and quickly spread across the country. The montreal games ended up leaving a 30-year legacy of debt and finan. Its total cost was an estimated $15 billion, which far surpassed the original budgeted amount. A significant portion of the overrun was due in part to the additional security costs incurred in the aftermath of 9/11. Furthermore, many of the profits realized by construction firms, hotels, and restaurants flow to international companies rather than to the local economy. The 2004 olympics in athens Another advantage of hosting the olympics is the impact on the host nations travel and tourism industry. For example, rio de janeiro constructed 15,000 new hotel rooms to accommodate tourists. At the time, experts estimated that latin america and the caribbean (which includes brazil) would experience a significant drop in tourism, resulting in as much as $64 billion in revenue with a loss of as much as $7 billion to $18 billion to the region between 2015 and 2017. Many spectators al. Rather, they represent ongoing expenses. Similarly, beijing’s bird’s nest arena costs $10 million in annual maintenance. In addition, when a city borrows to finance construction, it can be on the hook for. Cities hosting the olympics gain temporary jobs due to infrastructure improvements that continue benefiting the cities into the future. An in-depth look at the economic impact of hosting the olympics and whether the long-term benefits justify the massive costs for host cities.