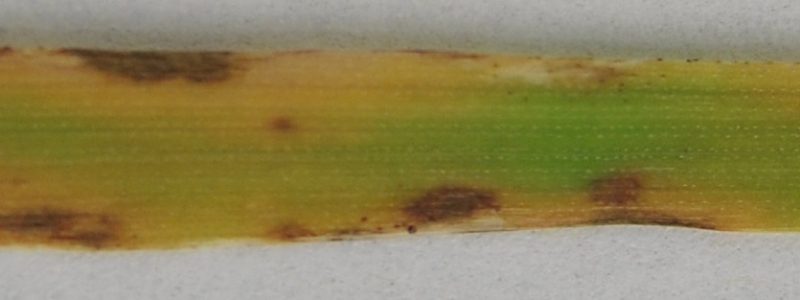
Oatleafblotchinfo suggest that the fungus overwinters in old plant material and occasionally from seed.OatLeafBlotchControl. Since it is most common in areas with oat stubble, it is important to completely till this into soil deeply. An infection of Septoria leafblotch of oats can significantly decrease grain yield and downgrade oaten hay quality, particularly in high-rainfall zones. The disease is caused by the fungus Parastagonospora avenae f. sp. avenaria. Leafblotch surveys Leafblotch diseases of oat are caused by a complex of Pyrenophora avenae, Cochliobolus sativus and Stagonospora (Septoria) avenae. The complex has become more prevalent in recent years. Tritici, Pyrenophora leafblotch caused by Pyrenophora chaetomioides, Septoria blotch caused by Phaeosphaeria avenaria, and Barley yellow dwarf virus transmitted by aphids. It describes the pathogens, symptoms, and management strategies for each disease... Occurrence of oatleafblotch in Texas in 1973. Plant Dis. Rptr.Author information. Authors and Affiliations. Plant Pathology and North Central Experiment Station, University of Minnesota, Grand Rapids, Minnesota, USA. oat most frequently (Farr and Rossman 2019). Besides leafblotch symptoms, P. chaetomioides can also cause leaf stripes or spots (Ellis 1971), elongated or irregular stem spots (Harder and Haber 1992), stem darkening at the nodes (black stem) leading to stem-break in severe cases... Abstract/Summary Over the four years (2014-2017) that field surveys were conducted in commercial oat fields to evaluate the prevalence of oatleafblotch pathogens P. avenae was the most often identified, being present in 59% of the 160 fields surveyed. This disease appears as reddish tan leafblotches that are somewhat linear with irregular margins. Heavily infected leaves die. Seedling blight may occur if coleoptiles are infected. 1974. Occurrence of oatleafblotch in Texas in 1973. The Plant Disease Report 58: 80-81. Hetherington, S. D., H.E. Smith, M.G. Scanes and B.A. Auld. 2002. Effects of some environmental conditions on the effectiveness of Drechslera avenacea. Biological Control 24: 103-109. Leafblotch disease symptoms in oat.Early results from the screening of several bi-parental populations indicate leafblotch disease resistance in oat is controlled by a single gene. Septoria leafblotch severity was assessed by estimating the percentage of leaf area affected, using an infection. key prepared by the senior author (Fig. 1). The leaf area diagrams were based on a range of leaf sizes and infection percentages of naturally infected oatleaves. Control of barley leafblotch is mainly through the use of fungicides with different modes of action. Early application of fungicides is only necessary for Autumn if early disease symptoms are severe.Leaf Spot (Pyrenophora avenae) is specific to oats. Septoria leafblotch occurs frequently and causes damage to oats in Alabama. This disease appears as brown, irregular-shaped blotches on leaves.Symptoms andcontrol are similar to those of leaf rust of wheat. None of the recommended varieties is resistant. Symptoms of red leafblotch (RLB), a plant disease caused by the fungus Polystigma amygdalinum, have been observed for the first time in California across the Northern San Joaquin Valley.