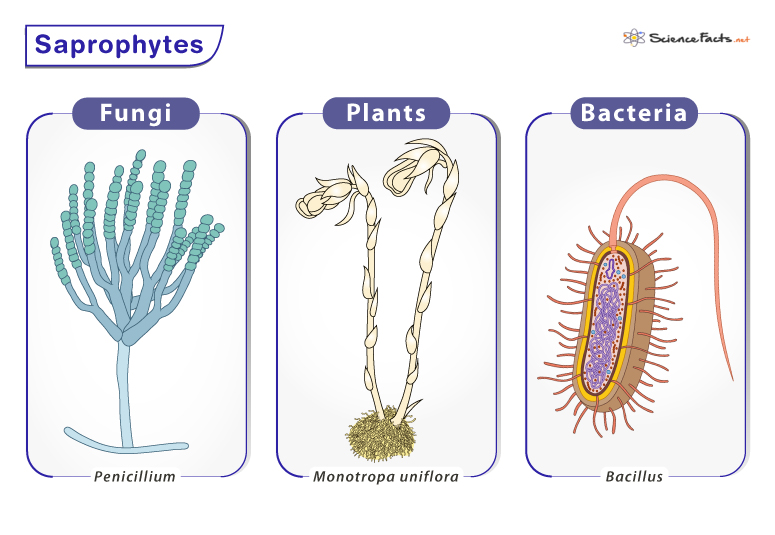
· But what exactly aresaprophytes, how do they function, and why are they important? This article explores the fascinating biology of saprophytes, their ecological roles, types, mechanisms of nutrient acquisition, and their significance in nature and human applications. As mentioned, saprophyte is an umbrella term used to refer to a number of organisms that feed on dead and decaying organic material (plant matter). The following are some examples of saprophytes: Fungi: Fungi and some of the most popular saprophytes. Some examples of saprophytic fungi include molds, mushrooms, yeast, penicillium, and mucor etc. Bac...See full list on microscopemaster.comAll saprophytes rely on dead and decaying plant matter for nourishment (partially or fully). While they have some similarities, there are differences between the different types. The following are some characteristics of the different types of saprophytes:See full list on microscopemaster.comThe majority of fungi are saprophytes and thus depend on dead and decaying organic matter for nourishment. Given that fungi do not have chlorophyll, they do not directly need sun energy which is necessary for photosynthetic plants. For this reason, they are often found in shady areas (e.g., underneath trees and other vegetation) where dead and deca...See full list on microscopemaster.comAs the name suggests, saprophytic bacteria are bacteria that break down or decompose organic matter. In particular, these organisms are capable of breaking down complex compounds like hemicellulose and lignin among others into simpler forms that they can then use or can be used by other organisms. Apart from saprophytic fungi, saprophytic bacteria ...See full list on microscopemaster.comAlso known as angiosperms, flowering plants represent the most common and diverse group of all land animals. While the majority of these plants are autotrophs, capable of manufacturing their own food, some obtain part of their nourishment from dead and decaying organic matter. One of the best examples of saprophytic flowering plants is the Ghost pl...See full list on microscopemaster.comAlgae is a large group of photosynthetic organisms that belong to the kingdom Protista. There are few saprophytic algae that belong to the genus Polytoma. Unlike most other algae, these saprophytic algae lack chlorophyll and are therefore incapable of photosynthesis. For this reason, members of this group rely on dead and decaying organic matter fo...See full list on microscopemaster.comAriana Kubartová, Jacques Berthelin, Thierry Beguiristain, and Jacques Range. (2008). Diversity and Decomposing Ability of Saprophytic Fungi from Temperate Forest Litter. Danièle Gaspard. (2011). Endolithic algae, fungi and bacterial activity in Holocene and Cretaceous brachiopod shells - Diagenetic consequences. Luana Cassandra. (2014). Saprophyti...See full list on microscopemaster.comSaprophytes are organisms that feed on dead and decaying organic matter, especially plant matter. Learn about the different types of saprophytes (fungi, bacteria, plants, algae) and their features, such as enzymes, reproduction, and metabolism.See full list on microscopemaster.comAug 3, 2023 · Saprophytes are organisms that decompose dead or decaying matter and absorb the nutrients. They include fungi, some plants, and certain bacteria. Learn how they differ from parasites and vultures, and what role they play in ecosystems. · Saprophytes contribute significantly to maintaining healthy ecosystems through decomposition. They break down dead plants, animals, and waste products, preventing the accumulation of organic material on Earth’s surface. · This article explains what saprophytesare, highlights the key characteristics that set them apart, discussed their ecological significance, and showcases examples of varied saprophytic organisms. What are saprophytes in biology?Saprophytes in biology are organisms that obtain nutrients by decomposing dead organic matter, playing a vital role in nutrient recycling and ecosystem functioning. In this article, we will cover the saprophytes plants, examples, characteristics, and more.What are the characteristics of different types of saprophytes?The following are some characteristics of the different types of saprophytes: The majority of fungi are saprophytes and thus depend on dead and decaying organic matter for nourishment. Given that fungi do not have chlorophyll, they do not directly need sun energy which is necessary for photosynthetic plants.How do saprophytes get their nutrients and energy?Saprophytes are a group of organisms that obtain their nutrients and energy by decomposing dead or decaying organic matter. Saprophytes examples include fungi like mushrooms, molds, and yeast. They form an important part of the nutrient cycle in ecosystems and release essential nutrients and energy stored back into the environment.Why is a saprophyte important to the ecosystem?Additionally, a saprophyte is helpful to the ecosystem because as it decomposes the bodies of dead organisms, it recycles and releases nutrients into the environment, making them available for other organisms to use. This is especially important for plant growth. Detritivore – An animal that lives off dead and decaying matter. · A saprophyte is an organism that feeds and grows on dead organisms, such as bacteria and fungi. Learn how saprophytes decompose organic matter, recycle nutrients, and take a quiz on related terms. · Saprophytes examples include fungi like mushrooms, molds, and yeast. They form an important part of the nutrient cycle in ecosystems and release essential nutrients and energy stored back into the environment. · Saprophytes are organisms that decompose dead or decaying matter and absorb the nutrients. They include fungi, some plants, and certain bacteria. Learn how they differ from parasites and vultures, and what role they play in ecosystems. · This article explains what saprophytesare, highlights the key characteristics that set them apart, discussed their ecological significance, and showcases examples of varied saprophytic organisms. · Saprophytes examples include fungi like mushrooms, molds, and yeast. They form an important part of the nutrient cycle in ecosystems and release essential nutrients and energy stored back into the environment. · Saprophytes contribute significantly to maintaining healthy ecosystems through decomposition. They break down dead plants, animals, and waste products, preventing the accumulation of organic material on Earth’s surface. · A saprophyte is an organism that feeds and grows on dead organisms, such as bacteria and fungi. Learn how saprophytes decompose organic matter, recycle nutrients, and take a quiz on related terms.